By Lisa Tryson and Torben Funder-Kristensen
Fluctuating environmental policies in the U.S. tend to obscure the fact that the transition toward refrigerants with a low global warming potential (GWP) continues. HVACR manufacturers, researchers and facility owners worldwide are making significant progress thanks to consistent public policies, but also from recent development of proven technologies.
Technologically, it’s worth looking at recent moves away from refrigerants with high GWPs—like HFC-134a and HFC-404A—and toward low-GWP formulations, like natural hydrocarbons and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) with GWPs below 5. The HFOs have a low GWP because they break down in the atmosphere over a few days. Furthermore, HFOs together with HFCs form low-GWP hybrids that have GWP ratings below 150.
Innovation is unlocking the potential of new refrigerants to create a low-GWP future. Important developments include: Utilizing the thermodynamics of CO2 refrigerant—specifically, its expansion energy and heating properties—to make CO2 even more feasible for commercial refrigeration; the ongoing decarbonizing of the electric power supply; and, boosting flexibility in electric consumption with demand response and thermal storage technologies. These are driving forward the adoption of low-GWP refrigerants in food and commercial refrigeration today.
Moving from concerns over ozone depleting to global warming refrigerants
Following the success of the 1987 Montreal Protocol enabling the transitions from high to low ozone depletion potential (ODP) refrigerants, the 2016 Kigali Amendment focused on transitioning from high- to low-GWP gases. The total impact of a cooling system on the environment can be measured through its Life Cycle Climate Performance (LCCP).
The LCCP number summarizes the direct impact of the production, usage and leakage of refrigerants, and the indirect emission caused by the production of the system (such as materials) and electricity consumed by the system. Under the 2016 Kigali Amendment, 197 countries committed to cut the production and consumption of hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerants, most of which have GWPs ranging from 675 to 3,985. In cutting HFC consumption by over 80% by 2047, the Kigali Amendment aimed to prevent a modeled 0.5°C increase in global temperature by the end of the century.
The U.S. has not yet ratified the Kigali Amendment, which went into effect Jan. 1, 2019. Nevertheless, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – through its 2016 Significant New Alternative Program (SNAP) rules – had banned the use of high-GWP HFCs in many types of commercial refrigeration systems, including supermarket and commercial food equipment. Subsequent lawsuits resulted in the EPA withdrawing the HFC ban in 2018. Nevertheless, several states are developing HFC phasedown rules. California has adopted EPA SNAP Rules 20 and 21 and will be implementing GWP limit-based rules in the future. Other states are seeking to implement those EPA SNAP rules, as well. Seven states have proposed or enacted 13 laws, regulations or plans since 2018.
Fluctuating policies pose a problem for HVACR equipment manufacturers. Regulatory consistency would help smooth the transition from high- to low-GWP refrigerants, which has been technologically challenging.
In the earlier transition from high to low ODP refrigerants, manufacturers could generally use a “drop-in” approach—that is, simply replacing one refrigerant for another after modifying seals and other minor components. That is not always possible with the switch to low-GWP refrigerants. Natural refrigerants, such as ammonia and CO2, operate with different parameters compared to HFCs and require specially-designed system components. Other natural refrigerants, such as propane, use components similar to those employed with HFCs, but special safety precautions need to be taken. Depending on corporate goals and local regulations, manufacturers and end-users worldwide are adopting low-GWP-refrigerant systems employing various technological innovations.
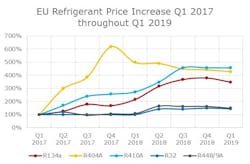
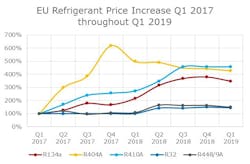
In the European Union, the progress of HFC phasedown has continued (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the phasedown was heavily challenged due to early stockpiling, misleading the market’s perception of HFC availability and unused HFC refrigerant quotas from 2015. Consequently, a large amount of new high-GWP equipment was still on the market. In 2017, the market experienced a steep price increase and HFC scarcity, both of which drove the first step of the phasedown (Figure 2). Finally, in 2018 and 2019, HFC consumption continued to drop, low-GWP refrigerant prices started to stabilize, and the conversion to low-GWP solutions gained momentum.
In 2018, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) supported the successful implementation of a CO2 refrigeration system in the store.
The region experiences 90°F (32°C) and higher ambient temperatures in the summer. Compared to using HFCs at those temperatures, employing CO2 refrigerant within its normally high operating pressures was not energy efficient. Nevertheless, several advanced technologies were employed to go beyond CO2’s traditional ambient temperature limitations. The system used the Danfoss Multi Ejector Solution™ consisting of a high-pressure valve, integrated pressure transmitter and an intelligent system controller in conjunction with the compressor rack. The system operates reliably in the transcritical zone of the compression cycle, where pressures can exceed 1,067 psia. In the transcritical zone, heat rejection can efficiently occur even at high ambient temperatures—even at 36°C (97°F). The bottom line: The CO2 system supplying display cabinets has an extremely low GWP of 1.0 and provides up to 30% energy savings compared to the incumbent solutions based on R-22 and R-404A refrigerants. A technology hub has been established to explore adopting the transcritical CO2 solution for air conditioning in the store.
Adding to the momentum are philanthropic-funded initiatives, such as the Kigali Cooling Efficiency Program (KCEP) promoting low-GWP solutions in developing countries. Other non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and academic institutions are also stepping up to help raise the level of innovation to define the HFC-free cooling technologies of the future.
Speed bumps in accelerating toward low-GWP refrigerants
Several HFO refrigerant formulations have been readily adopted for a number of applications. R1234yf is used by automotive manufacturers for car air conditioners. R1234ze(E) is used in innovative centrifugal compressors employing magnetic bearings, such as Danfoss Turbocor® compressors.
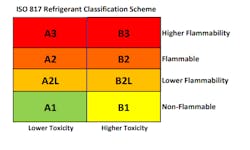
Some low-GWP refrigerants are flammable. Some are toxic. Some are both. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) 34 and International Standards Organization (ISO) 817 standards have been developed to classify flammability and toxicity (Figure 3). Lower GWP properties tend to correlate with higher flammability/toxicity characteristics. For example, HFC refrigerant R-410A (with a 2088 GWP) is non-toxic, non-flammable and classified A1. The HFO refrigerant R1234yf (with a 4 GWP) is non-toxic, mildly flammable and classified A2L. Hydrocarbon refrigerants (R-600a isobutane and R-290 propane) are highly flammable (A3). Ammonia (R-717) has higher toxicity and flammability (B2). CO2 (R-744) is an exception with no flammability or toxicity (A1).
The correlation between GWPs, refrigerant density (weight per volume) and safety classifications of various refrigerants is of great concern to HVACR system manufacturers and specifiers (Figure 4).
Blends of HFOs and HFCs are being developed to optimize performance and safety. Whether using HFOs, natural refrigerants or blends, HVACR manufacturers must innovate technologies that maximize efficiency and minimize risk for the selected refrigerant.
Development of new technologies make it easier for manufacturers to balance safety and environmental responsibility. Some leading retailers have been using R-290 (propane) in equipment for over a decade. Taking advantage of R-290’s excellent thermodynamic properties — such as volumetric capacity, capacity and coefficient of performance (COP)—systems are operating successfully with a charge limited to 150 grams (5 ounces) for safety. Further research and product development led the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) to propose a 500-gram (1.1-pound) limit for R-290 in single commercial refrigeration appliances. The new standard was re-voted and passed in May 2019.
As time passes, it’s logical to think that Europe and the U.S. will continue to explore the balance between safety, efficiency and the environment—but not at the expense of endangering users and technicians.
New design and safety measures are needed to avoid flammability in occupied spaces and during servicing. For over a century in the U.S., HVACR manufacturers and service technicians have been working with A1 refrigerants.
The service industry, in particular, will need to become more familiar with flammable refrigerants. “Installation and service are the areas where proper guidelines, training, certification and standards are the most important,” explains Bill Goetzler of Navigant Consulting. “The lines carrying flammable refrigerants may be opened during various servicing operations, and service personnel also may be working with a high-temperature ignition source. Those are really places to be very careful and to be sure we’ve got standards and guidelines in place to minimize the risk.”
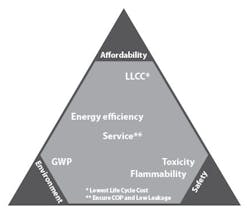
Safety is a vital factor relative in a refrigerant sustainability triangle that includes environmental and economic factors (Figure 5).
Other factors come into play depending on the properties of the refrigerant. With some HFO refrigerants, for example, flammability can present a safety issue, as previously discussed. Cost can also be a factor, as HFO formulations are more expensive to produce, and supplies are constrained. Finally, environmental concerns can still be an issue in several countries, because some HFOs break down in the lower atmosphere, forming fluorinated products. Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an HFO breakdown substance but also occurs naturally in seawater. Hydrogen fluoride (HF) is another HFO breakdown substance which is very toxic. The small amounts of TFA and HF are not expected to pose global or regional problems.
Four technological developments that can build a steady transition platform
The search for refrigerants that perfectly balance environmental, economic and safety concerns is continuing. Unfortunately, this quest throws customers and end-users off balance. Planning is stressful when the future is subject to change. Fortunately, in recent years, technology has developed to the point that it is possible to build a long-lasting platform for low-GWP commercial refrigeration. Proven technologies are now available in four areas:
2. Developments in Demand Response — The high usage of electricity by supermarkets can make it very advantageous to participate in demand response programs. As the name implies, in a demand response program, the utility sends a signal to a central control unit that utilizes the flexibility of the application to reduce power to motors, compressors and other electrical equipment. The signal triggers a reduction in electric consumption for brief periods ranging from less than one minute to long periods within a 24-hour interval, depending on the application.
Not every utility offers demand response programs. The utilities offering these programs pass on the prospective savings to participants. Economic benefits are based on the customer’s commitment to respond. A carefully designed demand response program using appropriate refrigeration control and management systems can achieve substantial energy savings while protecting food integrity.
For example, the Danfoss ADAP-KOOL® System Manager AK-SM 800 Series not only features a full web interface for remote monitoring and data management – it also incorporates built-in demand response capabilities that can take advantage of utility incentive programs. Additionally, it supports heat-reclaim technology and a variety of refrigerants, including CO2.
Store owners and energy managers should consult with utilities to evaluate their flexibility to shift the demand and the time of electric consumption.
3. Developments in thermal storage and related thermal-shifting technologies — Thermal storage makes it possible to shift electricity consumption from expensive peak rates during the day to lower rate periods during the night. Thermal storage tanks hold a liquid medium chilled at night for cooling display cases, reducing equipment run time.
In a supermarket application, the display cases can themselves function as a form of thermal storage. Lowering display-case temperatures during off-peak hours enables compressors to run less during peak hours. Thermal storage capacity can be used to produce a revenue stream when it’s connected to other stores through a district heating and cooling (DHC) system. Heat recovery technology can also be used to capture heat otherwise rejected by the refrigeration system’s condensers. For stores using CO2 with a heat-reclaim system, the size of a separate heat source—such as a boiler—can be greatly reduced or even eliminated.
4. Developments in the Decarbonized Grid — Called “the largest machine ever built,” the more than century-old electric grid is the largest producer of greenhouse gasses. Fortunately, technology exists today to re-engineer that machine to cut CO2 emissions dramatically. Increased use of renewable power (wind and solar), continued use of stable nuclear power and use of responsive hydropower are low-carbon resources that are gradually creating a decarbonized electricity supply. Models of a moderately decarbonized electricity system for the year 2050 estimate CO2 emissions intensity could be 60% to 80% lower than today’s U.S. grid.
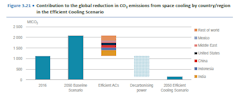
In the U.S., over 21 million kWh of electricity in 2017 was used in process cooling and refrigeration for food. By using low-GWP refrigerants, demand response and thermal storage technologies compatible with an increasingly decarbonized grid, air conditioning can help shrink its share of greenhouse gas emissions (Figure 6).
Conclusion: Recent technological developments are supporting the transition to low-GWP refrigerants. While policies may fluctuate, research and innovation are bringing proven products and platforms to market that can be implemented today in more food and commercial refrigeration applications than ever before. HFOs in conjunction with oil-free system developments are very viable options in air conditioning and, eventually, heat pump applications. Advances in transcritical CO2 systems are also providing an attractive value proposition for many supermarkets. Other developments—demand response, thermal storage and heat reclaim—complement the trend toward a decarbonized electric grid and significantly reduce commercial refrigeration’s carbon footprint. Utilities and regulators play a vital role in creating an HFC-free future. Incentives and policies can reassure supermarket owners operating on tight margins that their investment will pay off by boosting profits in the short term, as well as the environment in the long run.
Lisa Tryson is director, Corporate Communications & Public Relations, Danfoss. Torben Funder-Kristensen is head of Public & Industry Affairs, Refrigeration Controls Division, Danfoss.